Unlocking the Future: Pioneering Optical Sensors
In the realm of scientific innovation, the convergence of nanotechnology and optics has paved the way for groundbreaking advancements in sensing technology. Nanomaterials, with their extraordinary properties, have emerged as key players in the development of highly sensitive optical sensors, revolutionising various industries from healthcare to environmental monitoring. This newsletter delves into the transformative potential of nanomaterials as optical sensors, highlighting their distinct characteristics, integration into optical fibres, and impact on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through an exploration of their remarkable properties, deployment into optical fibres, and alignment with SDGs, we uncover the significant role nanomaterials play in shaping the future of sensing technology and fostering sustainable development.
Nanomaterials exhibit exceptional properties that make them ideal candidates for sensing applications. Metal oxides, such as zinc oxide and molybdenum oxide, boast high surface-to-volume ratios, facilitating enhanced interaction with target analytes. Their semiconductor nature enables precise detection through changes in electrical conductivity or optical properties. Similarly, MXenes, a class of two-dimensional materials, exhibit superior conductivity and surface chemistry, enabling rapid and selective sensing. Additionally, organic polymers offer tunable optical and electrical properties, rendering them versatile platforms for sensing diverse analytes. These examples underscore the versatility of nanomaterials in tailoring sensor performance to specific application requirements.
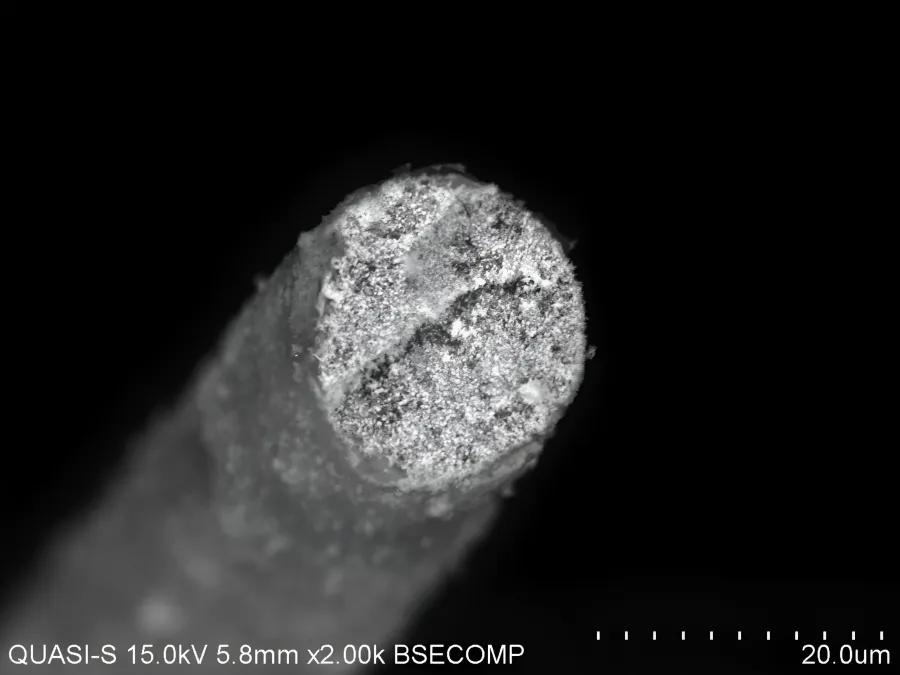

The integration of nanomaterials into optical fibres represents a paradigm shift in sensor design, offering numerous advantages such as miniaturisation, remote sensing capabilities, and real-time monitoring. By functionalising the fibre surface with nanomaterials, researchers can amplify the sensor's sensitivity and selectivity while maintaining flexibility and compatibility with existing optical systems. This integration enables seamless deployment in various environments, ranging from biomedical diagnostics to environmental monitoring, empowering users with real-time, actionable insights.
The utilisation of nanomaterial-based optical sensors aligns with several Sustainable Development Goals, addressing critical global challenges across multiple fronts. In environmental monitoring, these sensors facilitate the detection of pollutants, enabling proactive mitigation strategies and safeguarding ecosystems (SDG 14, Life Below Water; SDG 15, Life on Land). In healthcare, nanomaterial-enabled sensors offer early disease detection and personalised medicine, promoting health and well-being (SDG 3, Good Health and Well-being). Furthermore, the advancement of sensor technology fosters innovation and promotes sustainable industrialisation, driving economic growth and fostering resilient communities, in alignment with SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
As the transformative journey at the nexus of nanomaterials and optical sensing unfolds, an invitation is extended to passionate researchers, innovators, and stakeholders to shape the future of sensing technology. Together, harnessing the power of nanomaterials can address pressing societal challenges, drive sustainable development, and unlock new frontiers of scientific discovery. Whether experts specialise in nanotechnology, optics, or application domains such as healthcare or environmental monitoring, their expertise and collaboration are invaluable in propelling this research forward.
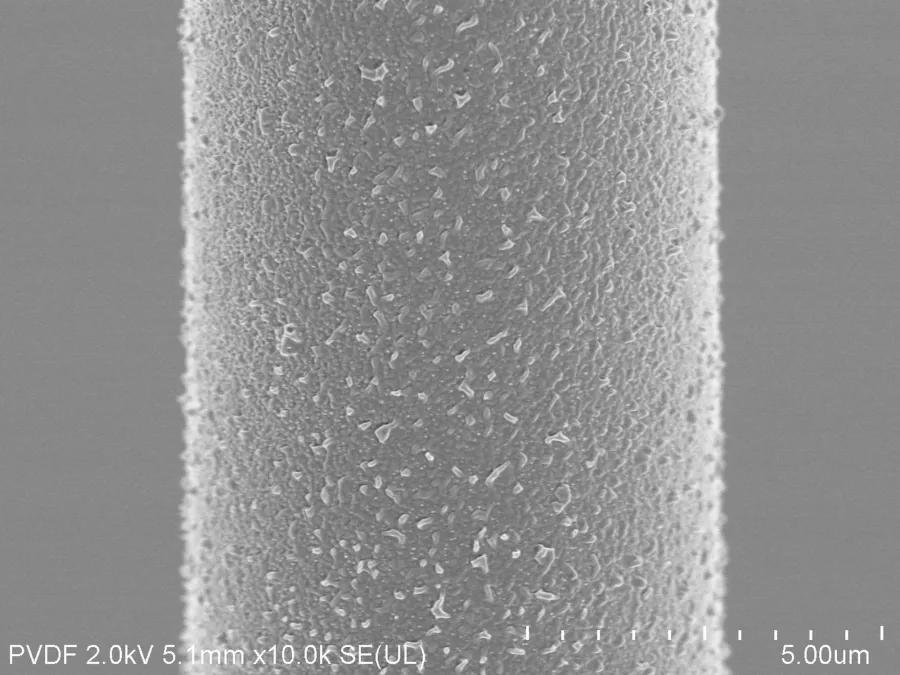
In conclusion, nanomaterials are recognized for their immense promise as the building blocks of next-generation optical sensors, offering unprecedented sensitivity, selectivity, and versatility. Integrating nanomaterials into optical fibres and addressing global challenges through collaborative research are pathways to realising the full potential of these sensors. Joining efforts in pioneering the future of sensing technology promises a brighter, more sustainable future for generations to come, where innovation knows no bounds.
Ts. Dr Nor Akmar binti Mohd Yahya
School of Engineering and Technology
Email: @email




